Single Phase Isolation Transformer, 500 VA-30 kVA



Single-phase isolation transformers have good electrical isolation performance, which can effectively isolate input and output circuits and provide additional safety protection. Moreover, they have stable voltage conversion capability to convert the input voltage to the required output voltage, adapting to different power system requirements. We offer single-phase isolation transformers, manufactured in Chinese facilities, ranging from 500 VA to 30 kVA, and can customize transformers to meet the different needs of our customers.. Whether it is for industrial applications, commercial buildings or residential use, we have the right solution for our customers.
Specification
| Basic Parameters | Model | ATO-T-DG |
| Phase | single phase | |
| Capacity | 500 VA-30 kVA (customized) | |
| Winding Material | Aluminum/copper wire (customized) | |
| Frequency | 50Hz / 60Hz | |
| Work Efficiency | ≥95% | |
| Primary Voltage | 0V-690V (customized) | |
| Secondary Voltage | 0V-690V (customized) | |
| Technical Parameters | Cooling Mode | Natural or air cooling |
| Insulation Resistance | ≥50 MΩ | |
| Electrical Strength | 2000V AC/1 min | |
| Noise | ≤35 dB (1 meter) | |
| Insulation Grade | Grade B (130℃), Grade F (155℃), Grade H (180℃) |
(Note: If you want to know more about single phase isolation transformer specification, please check in catalogue.)
Schematic Diagram
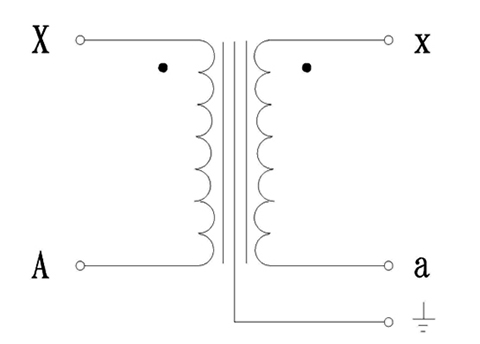
Dimension

- Without Enclosure: a*b*c=150*160*180mm
- Mouting Size: D*E=120*115mm (aperture: 15*8mm)
- With Enclosure: A*B*C=250*360*420mm
- Without Enclosure: a*b*c=132*140*150mm
- Mouting Size: D*E=100*110mm (aperture: 12*7mm)
- With Enclosure: A*B*C=200*320*420m
Advantages


Quality Assurance

Excellent Material

Fast Delivery

Multiple Models

Great Service
Design Key Points
- Cores. We can provide single phase isolation transformers comprising laminated or toroidal cores. The laminated cores feature several alternating layers of steel laminations, as well as insulations. These insulated cores help confine eddy currents and reduce the effect of magnetizing currents.
- Mounting. The isolation transformers can be provided in various mounting configurations. These isolation power transformers are widely used for circuit board applications, and they transfer voltages between different circuits.

Focus on Quality
Pending the need to increase or decrease input voltages, ATO's step-up and step-down transformers are dual frequency rated for 50/60 Hz and manufactured in a variety of configurations that range from 110 to 240 primary volts and from 110 to 240 secondary volts. Constructed with state-of-the-art technologies by experienced personnel consisting of electrical, mechanical and testing engineers, our step up and down transformers will last a long time.
FAQs
Difference between 1 phase isolation transformer and conventional transformer
- Electrical Isolation: The primary function of an isolation transformer is to provide electrical isolation between the input and output circuits. This means that there is no direct electrical connection between the primary and secondary windings. In a conventional transformer, the primary and secondary windings are typically connected by a magnetic circuit, allowing for voltage transformation but not electrical isolation.
- Voltage Transformation: Both isolation transformers and conventional transformers can be used for voltage transformation. However, isolation transformers are specifically designed to provide isolation while transforming voltage. They maintain a 1:1 turn ratio between the primary and secondary windings, meaning the output voltage is the same as the input voltage. Conventional transformers, on the other hand, can have different turn ratios to step up or step down the input voltage as required.
- Safety and Grounding: Isolation transformers are commonly used in applications where safety is a concern. By providing electrical isolation, they can help protect equipment and personnel from electric shock hazards. Isolation transformers can also be used to break ground loops, which can eliminate unwanted noise or interference in electrical systems. Conventional transformers do not offer the same level of isolation and are not specifically designed for safety or ground loop elimination.
- Size and Weight: Isolation transformers are typically larger and heavier than conventional transformers of similar power rating. This is because isolation transformers require additional insulation and separation between the primary and secondary windings to ensure proper isolation. The added insulation materials and construction increase the size and weight of the transformer.
- Applications: Isolation transformers find applications in various fields where electrical isolation and safety are critical, such as medical equipment, laboratory instruments, and sensitive electronic devices. They are also commonly used in telecommunications and audio equipment to eliminate ground loops and reduce noise. Conventional transformers, on the other hand, are widely used in power distribution, voltage conversion, and various industrial applications where electrical isolation is not a requirement.
In summary, the key differences between a 1-phase isolation transformer and a conventional transformer lie in their primary function of providing electrical isolation, the 1:1 turns ratio for voltage transformation, enhanced safety features, and larger size and weight due to insulation requirements.
How does a single phase isolation transformer provide electrical isolation?
- Construction: An isolation transformer consists of two separate windings, known as the primary and secondary windings, which are wound on a laminated iron core. These windings are electrically isolated from each other, meaning there is no direct electrical connection between them.
- Voltage transformation: When an AC voltage is applied to the primary winding, it generates a magnetic field in the core. This magnetic field induces a voltage in the secondary winding based on the turn ratio of the transformer. The primary and secondary windings can have different numbers of turns, allowing for voltage transformation (step-up or step-down) between the input and output.
- Electrical isolation: The key feature of an isolation transformer is that the primary and secondary windings are physically separated and electrically isolated. This means that there is no direct electrical path between the input and output sides of the transformer. The only connection between the primary and secondary circuits is through the magnetic flux in the core.
Can a single phase isolation transformer be used with sensitive electronic equipment?
- Electrical isolation: The primary purpose of an isolation transformer is to provide isolation, which helps protect sensitive equipment from electrical noise, surges, and other disturbances that may be present on the input power line. This isolation helps prevent such disturbances from propagating to the equipment connected to the output side, reducing the risk of damage or interference.
- Grounding issues: Isolation transformers can help mitigate grounding issues that may affect sensitive electronic equipment. By isolating the equipment from the power source's ground, it can prevent ground loops and related problems that can cause noise, hum, or interference.
- Voltage regulation: Some isolation transformers include voltage regulation capabilities, which can help stabilize the output voltage supplied to the connected equipment. This is particularly useful in areas where the input voltage may fluctuate or experience voltage sags or swells. Stable voltage levels are essential for sensitive electronic equipment to operate reliably.
However, it's important to note that while an isolation transformer provides electrical isolation, it does not provide any power conditioning or surge protection features beyond what the isolation itself offers. If your sensitive electronic equipment requires additional protection against power surges, voltage spikes, or other power quality issues, you may need to consider using a combination of an isolation transformer and other protective devices, such as surge protectors or voltage regulators.
What are the primary applications of a 1 phase isolation transformer?
- Safety: Isolation transformers are often used in situations where electrical safety is critical. By electrically isolating the input and output circuits, they prevent the flow of dangerous voltages or currents from one circuit to another, protecting equipment and individuals from electric shocks.
- Ground loop elimination: Isolation transformers can help eliminate ground loops, which occur when multiple devices in a system are connected to different ground points, causing unwanted currents to flow. By breaking the electrical connection between the input and output circuits, an isolation transformer prevents the ground loop from forming and reduces the associated noise and interference.
- Voltage regulation: Isolation transformers can also be used to regulate voltage levels. By adjusting the turns ratio between the primary and secondary windings, the output voltage can be stepped up or stepped down relative to the input voltage. This can be beneficial in situations where a stable and regulated voltage supply is required.
- Noise reduction: Isolation transformers are effective in reducing electrical noise and interference. They can isolate sensitive equipment from external noise sources, such as electromagnetic interference (EMI) or radio frequency interference (RFI), ensuring cleaner and more reliable power for sensitive electronics.
- Signal integrity: In some cases, isolation transformers are used to maintain signal integrity in communication systems.
By isolating the input and output circuits, they prevent signal distortion or degradation caused by impedance mismatches or ground loops, allowing for more accurate data transmission.
How is a 1 phase isolation transformer different from a regular transformer?
The primary difference between a 1 phase isolation transformer and a regular transformer lies in their primary function and design. While both transformers transfer electrical energy between circuits, a regular transformer is primarily used for voltage conversion, whereas an isolation transformer focuses on providing electrical isolation.
Here are some key differences between a 1 phase isolation transformer and a regular transformer:
- Electrical Isolation: The main purpose of an isolation transformer is to separate the primary and secondary windings electrically. This isolation helps protect sensitive equipment and personnel from electrical shocks and reduces the risk of ground loops. In contrast, a regular transformer does not provide electrical isolation as its primary purpose.
- Voltage Conversion: Regular transformers are commonly used for voltage conversion, stepping up or stepping down the voltage levels between the primary and secondary circuits. They are often found in power distribution systems to adjust voltages according to specific requirements. Isolation transformers, on the other hand, are typically used to maintain the same voltage level between the primary and secondary sides while providing isolation.
- Winding Configuration: Both isolation transformers and regular transformers can have different winding configurations, such as step-up (increasing voltage) or step-down (reducing voltage) configurations. The primary and secondary windings of a regular transformer are typically wound on a shared magnetic core, allowing for efficient energy transfer. In an isolation transformer, the primary and secondary windings are usually wound separately on the same core, ensuring electrical isolation.
- Grounding: Isolation transformers often include a dedicated grounding terminal to enhance safety. This grounding terminal helps to isolate the secondary circuit from the primary circuit and reduces the risk of electric shock. In regular transformers, grounding may or may not be required, depending on the specific application and electrical system requirements.
Overall, the primary distinction between a 1-phase isolation transformer and a regular transformer is the focus on electrical isolation in the former and voltage conversion in the latter. Isolation transformers are commonly used in sensitive applications where safety and protection against electrical shocks are crucial, while regular transformers are employed for voltage regulation and power distribution purposes.
Can a 1 phase isolation transformer be used in both residential and commercial settings?
- Electrical safety: It helps protect against electric shock hazards by isolating the output circuit from the input circuit. This is particularly important in settings where there is a risk of electrical faults or contact with exposed conductive parts.
- Noise reduction: An isolation transformer can help reduce electrical noise and interference, as it provides a barrier against common-mode noise and voltage spikes. This can be beneficial in both residential and commercial environments where sensitive equipment may be affected by such disturbances.
- Grounding flexibility: By using an isolation transformer, you can create a separately derived system with its own grounding point. This allows for greater flexibility in grounding practices, which can be useful in both residential and commercial applications where specific grounding requirements or local codes must be met.
While the primary function of an isolation transformer remains the same regardless of the setting, the specific requirements and ratings may differ between residential and commercial applications. It's essential to consider factors such as the load capacity, voltage rating, and any applicable safety standards or regulations to ensure the transformer is suitable for the intended application.



