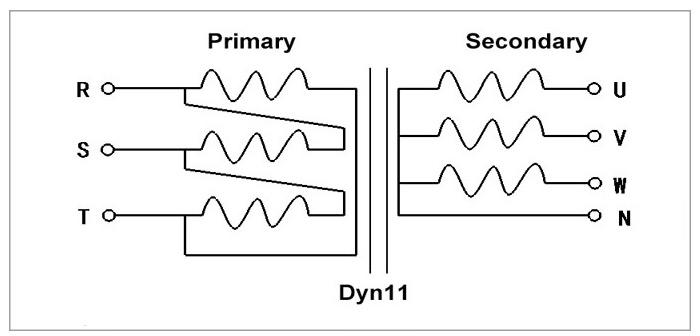
The common ratings of 3 phase isolation transformers can vary depending on the
specific application
and the country or region where they are used. Here are a few common ratings for 3
phase isolation
transformers:
-
Power Rating: The power rating of 3 phase isolation transformers is
typically expressed in
kilovolt-amperes (kVA) or megavolt-amperes (MVA). Common power ratings
include 5 kVA, 10
kVA, 25 kVA, 50 kVA, 100 kVA, 250 kVA, 500 kVA, 1 MVA, 5 MVA, etc. Higher
power ratings are
also available for industrial and utility-scale applications.
-
Voltage Rating: The voltage rating of a 3 phase isolation power transformer
refers to the
maximum voltage that it can handle. Common voltage ratings include 208V,
240V, 480V, 600V,
2.4 kV, 4.16 kV, 6.6 kV, 11 kV, 13.8 kV, 33 kV, etc. The specific voltage
rating depends on
the requirements of the electrical system in which the transformer will be
used.
-
Frequency: 3 phase isolation transformers are designed to operate at
specific frequencies.
The most common frequency ratings are 50 Hz and 60 Hz, which correspond to
the standard
power system frequencies in different regions of the world.
-
Cooling Method: Transformers may have different cooling methods, such as
air-cooled or
liquid-cooled. The cooling method affects the transformer's ability to
dissipate heat
generated during operation and can vary based on the transformer's power
rating.
These are just some common ratings for 3 phase isolation transformers. It's
important to consult
with our qualified electrical engineer to determine the appropriate ratings for your
specific
application, as requirements can vary based on factors such as load, voltage,
current, and
environmental conditions.